Refrigerators help us in the routine tasks of keeping our food fresh and drinks cold. However, have you ever sat down to think how these complex machines operate? The answer is concealed within the realm of thermodynamics— the science regarding the movement of heat and transfer of energy. This article focuses on the application of thermodynamic principles by refrigerators in order to keep them in low temperatures and ranges.
Key Takeaways
Refrigerators rely on the basis of thermodynamics to function, which states that energy should be used to transfer heat from the inside to the outer section.
The refrigeration cycle consist of four fundamental components which are: a compressor, condenser, expansion valve and evaporator.
Every process has to follow a certain law, in this case the an intervention by thermodynamic laws to govern the refrigeration process is critical to allow for efficient energy and heat transfer.
Recent advances in technology have made it possible for refrigerators to be more energy friendly and greener.
Familiarize yourself with the concepts concerning the thermodynamic principles of a device in order to reduce the energy consumption of the appliance.
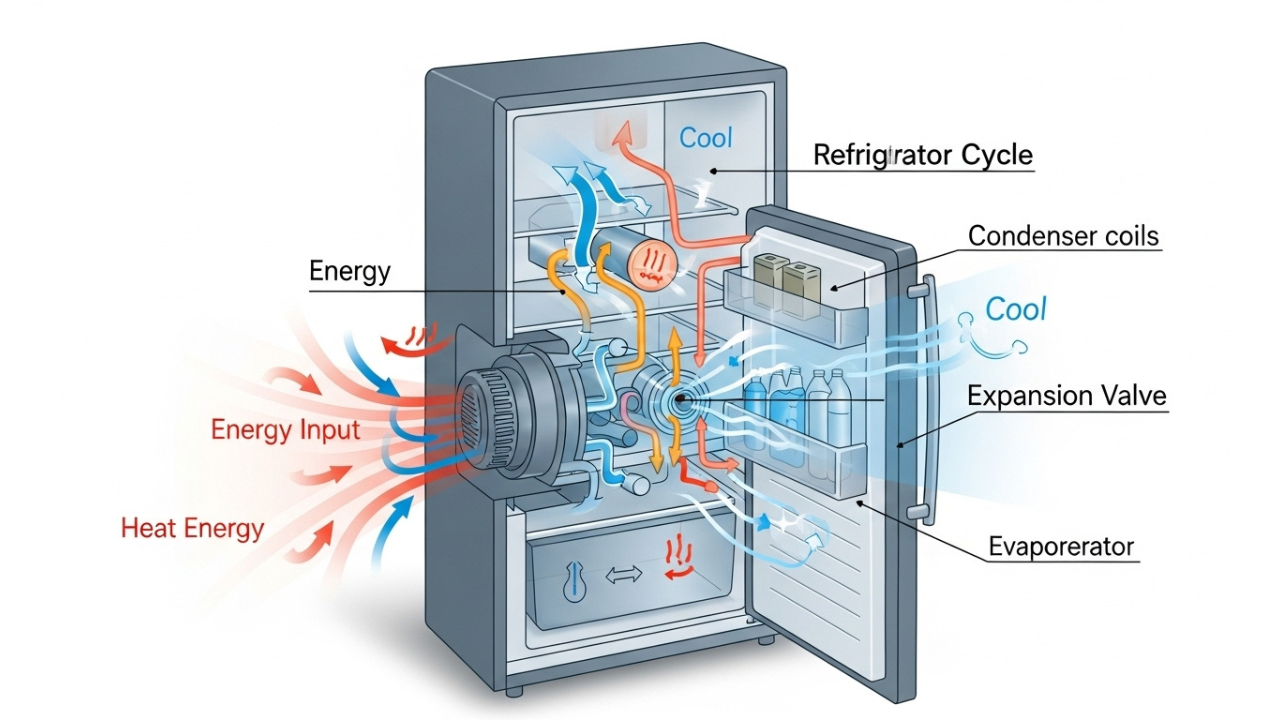
Understanding the Refrigeration Cycle
Heat transfer activities make a refrigerator work. It is encased in a closed loop system containing two water like fluids called a refrigerant which circulates in low boiling vessels. The components include a compressor, condenser, expansion valve and an evaporator
1. Compression of Refrigerant
Heat transfer activities make a refrigerator work. It is encased in a closed loop system containing two water like fluids called a refrigerant which circulates in low boiling vessels. The components include a compressor, condenser, expansion valve and an evaporator
2. Heat Dissipation in the Condenser
Heat transfer activities make a refrigerator work. It is encased in a closed loop system containing two water like fluids called a refrigerant which circulates in low boiling vessels. The components include a compressor, condenser, expansion valve and an evaporator
3. Expansion and Cooling
Expansion valves which are set at higher pressure than other region, are at first located after pre expanding region which works in conjunction with the evaporator. Expandable bulbs are also similar to interface with the evaporators and pumps. They have les difficulty due to low pressure sign send.
Using the relief valve give the evaporator tank the pressure given set-off level that makes them significantly increase their pressure and temperature, the pressure decreases below a point P0, at this point the pressures tend to move on the valve. As a result, this is the point which is the most crucial cooling effect is obtained.
4. Heat Absorption in the Evaporator
The refrigerant that has been cooled enters the evaporator coils located within the refrigerator. While evaporating, it takes in heat from the refrigerator’s interior, thus decreasing its temperature. After this, the refrigerant goes back to the compressor and the same process starts again.
Thermodynamic Principles at Work
Engineering and technology reside within each of your fridges: more specifically, thermodynamics. The branch of physics concerned with the movement of heat and energy changes is called thermodynamics. How a refrigerator works demonstrates the application of science techniques, and its role in removing heat from a specified area (in this case your fridge) and releasing it into the ambient air is no exception.
Let’s summarize the two thermodynamic laws which describe the functioning of a refrigerator.
First Law of Thermodynamics
Otherwise known as the law of energy conservation, this simply explains that energy cannot be generated or demolished, it can only change its state.
When you plug your fridge, it uses electrical power. The electrical energy feeds the fridge and when turned on, the compressor (a type of miniature pump) uses this energy to perform work. The compressor ‘sucks in’ the refrigerant (the special fluid circulating in the cooling system) and that action occurs due to thevation of electric energy into mechanical energy.
Apart from being a new form, electrical energy is also kinetic. The refrigerant takes heat from within the fridge and releases it externally or outside. As plugged in the fridge looses electrical energy but in return ceases to be in the form of moving heat fuel powered by commanded energy. Therefore, the energy used here is not being wasted at all.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
As The Second Law of Thermodynamics states, heat always flows from areas of higher temperature to areas of lower temperature unless work is done to reverse this natural process.
If an object is kept in a warm room, the heat emanating from the room will gradually warm the object and it will become warmer. Heat will always intent to flow toward areas of lower temperatures.
A refrigerator is a heat transfer tool of the reverse kind. It takes the heat from the cold space inside the fridge and puts it into the warmer surroundings. For the heat to move this way, energy needs to be supplied. This is the function of the compressor and refrigerant. They perform the work that is required to shift the heat from its natural direction. This is what the second law explains; to move heat from cold to warm regions in an unnatural way requires additional energy to be supplied.
Efficiency Considerations
When you think of a refrigerator, it is likely that you expect it to keep your food cold. Behind the scene, however, a lot of engineering has been done to ensure that the refrigerator does the job with reasonable consumption of electricity. Modern refrigerators are designed with energy efficiency features. This implies that they are made to do more while consuming less energy, a situation beneficial to your energy bill as well as the environment.
An expert may assess how well energy is utilized by a refrigerator by checking its Coefficient of Performance, or COP, figure. This ratio indicates how much heat the refrigerator removes from the inside in comparison to the energy spent removing it. The COP remaining high guarantees the refrigerator operates effectively.
The refrigerants in modern refrigerators are different. These are the fluids used in the microwave which should be circulated in the refrigerator. The older types of refrigerants were harmful to the ozone layer as well as contributed to environmental warming. Because the newest models are much kinder to the refrigerants, today’s models are more environmentally friendly.
The other big improvement is the use of inverter compressors. The former version of installing a fridge came with a compressor that would turn it on and off. With inverter, compressors can speed and slow down based on the need for cooling.
Cold air insulation also received impacts in the past 10 years or so. More advanced materials designed to keep the Cold air in the fridges make it possible for less effort from the compressor. This leads to a prolonging device life along with energy savers.
Hence, when purchasing or servicing a refrigerator, it is wise to consider its energy conservation capabilities. An energy-efficient refrigerator saves on electricity expenditure, operates more quietly, and has a longer lifespan.
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
Even the latest model of a refrigerator requires a certain amount of attention and care. Much like a vehicle requires oil changes, a refrigerator requires simple routine checkups. These procedures, while easy and simple, can greatly improve the performance of the refrigerator and the amount of energy it consumes.
Clean the Condenser Coils
Have you ever peeked behind or under your fridge for a good look at the condenser coils? If you have, then you must have noticed an unsightly layer of dust which is usually found there. When they are covered in dust, the fridge will lack the ability to easily get rid of heat. The compressor ends up working harder which increases energy expenditure. Coils can be cleaned every couple of months using a vacuum or brush and this will help the fridge run more efficiently.
Check the Door Seals
If cold air is able to escape by leaking out, the refrigerator will need to work double hard in order to maintain the temperature. When these door seals also referred to as gaskets become worn out or dirty, this is exactly what happens. Use a dollar bill to close the door check the sealing. If the bill slides out easily, then it may be high time to replace the seals. Clean and well-maintained seals allow for the maintenance of the cool air being inside the fridge.
Keep Things Organized
Although you might not notice, the way food is organized within your refrigerator is of the utmost importance. With air circulation, everything within the fridge gets cooled evenly. Overstuffing the refrigerator blocks airflow, and makes the compressor work overtime cooling staff that do not fit. Try to keep the spacing and avoid stacking the items tightly.
Set the Right Temperature
Although you might not notice, the way food is organized within your refrigerator is of the utmost importance. With air circulation, everything within the fridge gets cooled evenly. Overstuffing the refrigerator blocks airflow, and makes the compressor work overtime cooling staff that do not fit. Try to keep the spacing and avoid stacking the items tightly.
My Opinion
The science of food refrigeration encourages understanding of principles such as thermodynamics since these keep food and drinks fresh and cool. Adhering to thermodynamics allows fridges to seamlessly transfer heat and maintain required temperatures within. Performing regular maintenance and being conscious of energy-saving steps help in maximizing fridge efficiency and increasing their lifespan.
Please reach out to me if you have any questions, or require further information, regarding refrigerator maintenance.






























Leave a Reply
View Comments